这篇文章也是参考了 https://javadoop.com/post/AbstractQueuedSynchronizer-2 这篇文章,总结思路。
Condition的实现原理
condition的一个简单的demo如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| class BoundedBuffer {
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
final Object[] items = new Object[100];
int putptr, takeptr, count;
public void put(Object x) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
items[putptr] = x;
if (++putptr == items.length) putptr = 0;
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public Object take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
Object x = items[takeptr];
if (++takeptr == items.length) takeptr = 0;
--count;
notFull.signal();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
|
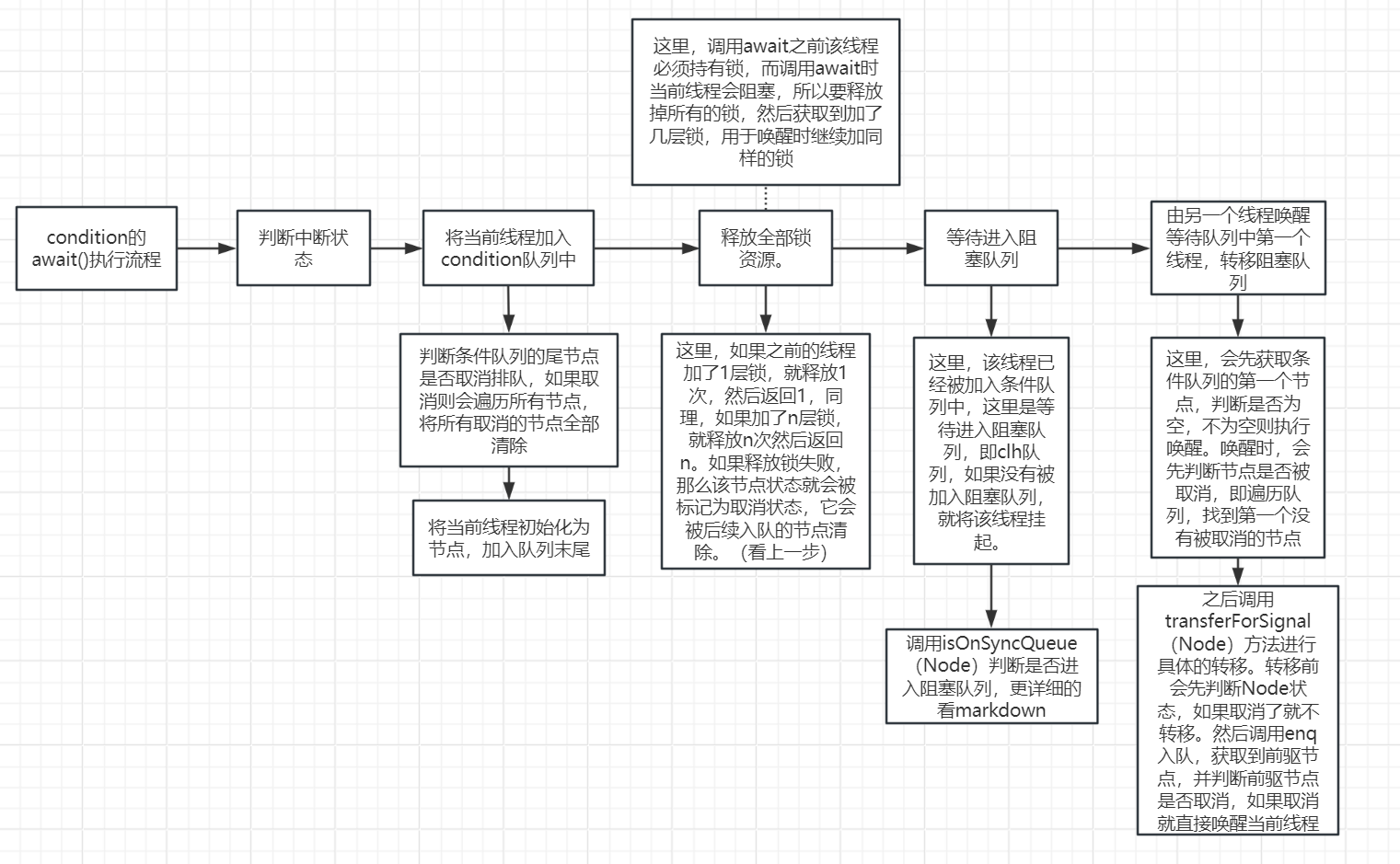
不难看出,在使用 condition 时,必须先持有相应的锁。

如上图所示,如果一个调用condition.await(),那么调用该方法的线程会被包装为一个Node,然后加入condition1的条件队列中,然后阻塞在这里。如果调用了condition.signal(),那么会唤醒对应condition队列中第一个节点,然后将其加入阻塞队列的末尾,等待获取锁然后执行。
condition的await实现流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;
if (node.next != null)
return true;
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {
Node t = tail;
for (;;) {
if (t == node)
return true;
if (t == null)
return false;
t = t.prev;
}
}
|


